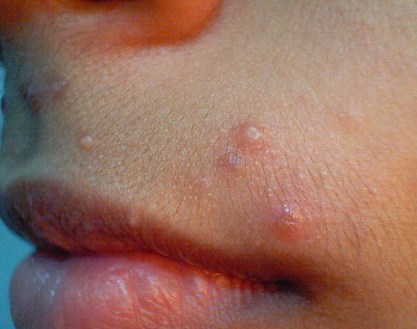
We are sometimes contacted with questions about cimetidine molluscum treatment. Cimetidine is not a very commonly-prescribed molluscum contagiosum treatment, but sometimes doctors do recommend it. We’ll tell you about the pros and cons of using cimetidine to treat molluscum. We’ll also tell you about some of the alternatives.
What is Cimetidine?
Cimetidine is a drug, available both by prescription and over the counter, to treat heartburn, indigestion, GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), ulcers, and related disorders. It has also been found to have antiviral properties, though it has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum or any other viral infection. When doctors prescribe cimetidine for that purpose they are said to be prescribing it “off label,” which is legal and fairly commonly done with a wide variety of drugs.
Benefits of Cimetidine Molluscum Treatment
Cimetidine is more affordable than some other prescription antiviral drugs, especially since it can be purchased over the counter. Note that we do not recommend using cimetidine to treat molluscum unless advised by your doctor, however. Do not go to the drug store and buy some over the counter and treat yourself. Consult your doctor first and follow all instructions carefully.
Cimetidine may carry a lower risk of side effects than some other antiviral drugs, as well. It can still cause side effects in some people, though.
An oral medication like cimetidine is preferable to treatments like cryotherapy (burning off molluscum bumps) and laser treatments for molluscum to many people since those treatments can cause pain and scarring. Oral medication is also easier to use than topical medications, which must be carefully applied to each molluscum bump.
Risks of Cimetidine Molluscum Treatment
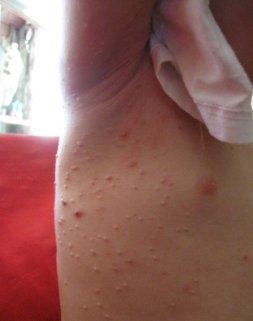
Not everyone should use cimetidine. It is often not recommended for people with immune system problems, kidney problems, liver problems, and some types of lung disease. It is not recommended for children under the age of 12 (and molluscum is most common in children ages 10 and under) and the risk of serious side effects is greater in elderly people. It may not be safe to take if pregnant or breastfeeding.
Cimetidine reduces the production of stomach acid, which in turn can reduce the absorption of some vitamins and minerals, including iron, some forms of calcium, and vitamin B12. If you have anemia or other nutritional deficiencies or need to take any vitamin or mineral supplements, talk to your physician about how to maximize absorption while taking cimetidine.
Alternatives to Cimetidine Molluscum Treatment
Alternatives to cimetidine for molluscum include other oral antiviral drugs, topical medications, natural remedies, and minor surgical procedures such as scraping or freezing off the bumps. Laser therapy is another option. There are risks and benefits to all of these treatment options, of course. You can learn more about treatment options for molluscum. We also encourage you to discuss your options, including risks, benefits, and alternatives, with your physician.
Our Preferred Molluscum Contagiosum Treatment
Our preferred treatment for molluscum is a natural remedy called Naturasil. While even the gentlest of natural remedies can trigger allergic reactions or cause unwanted side effects in some instances, the risk of serious side effects is significantly less than with prescription medications like cimetidine. Naturasil is easy to use and does not cause pain or scarring. Just follow this link to learn more about Naturasil and see if it might be right for you.
(1)Medicinenet: Cimetidine Side Effects
