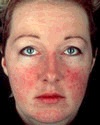
What is acne rosacea? It’s one of four subtypes of rosacea. In addition to acne rosacea, or papulopustular rosacea, other subtypes include erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (reddened, irritated skin with very visible blood vessels), phymatous rosacea (skin tissue thickens, especially on the nose) and ocular rosacea (eyes are red, dry, and irritated and the lids may be swollen). It’s possible to have more than one subtype or set of symptoms, but for now, we’ll tell you all about papulopustular rosacea and about your acne rosacea cure options.
What is Acne Rosacea?
As explained above, acne rosacea is technically called papulopustular rosacea and it is one of four subtypes of rosacea. It causes small, pus-filled bumps on the face that resemble acne and in fact, rosacea is sometimes mistaken for acne or misdiagnosed as acne because of this.
Papulopustular rosacea may also affect the neck, chest, and/or back. Usually, it starts on the face but it may slowly spread down to other areas. In addition to the small, pus-filled bumps, papulopustular rosacea causes redness and swelling. Your skin may also feel uncomfortably warm and tender or sore to the touch.
Finding an Acne Rosacea Cure
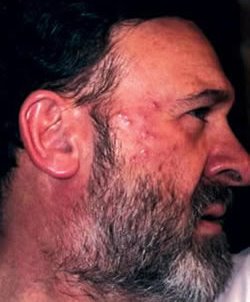
Now that you understand what is acne rosacea, you’re probably wondering how you cure it. Unfortunately, there is no cure for rosacea, not for any of the subtypes. There are treatments, though, that can reduce symptoms and relieve the discomfort associated with rosacea. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, rosacea often gets worse over time without treatment, so even though there is no cure, it’s still worth seeking treatment to improve your comfort as well as your appearance and to prevent your condition from worsening.
When talking about acne rosacea, it’s especially important to treat the condition because the pus-filled bumps can lead to scars. Finding an effective treatment can prevent permanent damage to your skin.
Isotretinoin
An acne medication called isotretinoin is sometimes prescribed to treat acne rosacea. Isotretinoin can cause serious side effects, though, some of them life-threatening. Not all people experience serious side effects, of course, but unfortunately, there is no way to predict who will and who won’t. Potential side effects of isotretinoin include nosebleeds, achy joints, high cholesterol, hepatitis (inflammation of the liver), and swelling of the brain. Some people have also experienced psychiatric side effects, like severe depression and hallucinations. In some cases, people have died or become permanently disabled as a result of this medication. Isotretinoin can also cause severe birth defects and women should make sure they do not become pregnant while taking this drug.
Alternatives to Isotretinoin
You can understand why people want an alternative to isotretinoin to treat their acne rosacea. You can also understand the importance of treating it with something that is effective. Sometimes antibiotics help, since the acne-like bumps associated with rosacea may be caused by clogged and infected skin pores. Sometimes anti-inflammatory drugs help, too, although those are better for reducing the redness and swelling that accompanies rosacea than for getting rid of the pus-filled bumps associated with papulopustular rosacea. While antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are generally safer than isotretinoin, unfortunately, they often aren’t very effective for acne rosacea.
Our preferred treatment for acne rosacea is the Zenned Skin Support System. Because it contains all-natural ingredients, like cucumber, green tea, organic aloe vera gel, willow bark extract, rosehip oil, jojoba oil, lavender, evening primrose, and tea tree oil, the risk of side effects is very low and even if they occur, they are much milder than the side effects of isotretinoin. At the same time, the natural ingredients work together to treat most of the common symptoms of rosacea, including acne, redness, swelling, inflammation, itching, irritation, and tenderness. To learn more about our preferred treatment, just follow this link to the Zenmed Website.
AAD: Rosacea
